Osteochondrosis is a disease of the skeletal system characterized by changes in cartilage tissue. As the disease progresses, a person’s ability to work decreases, blood circulation and the integrity of the spinal discs are disrupted. Most often, the disease develops in obesity, physical inactivity, frequent spending time at the computer or driving a car.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, during its development, is characterized by the following symptoms: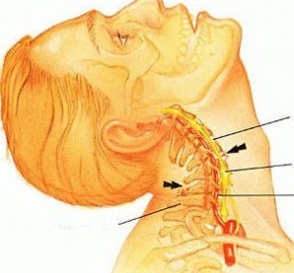
Neck pain with cervical osteochondrosis
- continuous headache. Patients with osteochondrosis mostly have headaches that are exacerbated by a sharp twist of the neck or a sudden movement of the head.
- Neck pain that may radiate to the shoulder area. It often appears in the morning, at bedtime, cools down or disappears altogether after warming the neck muscles.
- Cervical lumbago is characterized by severe pain in the neck, tightening of the muscles in the injured area and limited mobility.
- Pain in the bump or gallbladder. Patients most often suspect they have pathology of the cardiovascular system, but taking nitroglycerin does not relieve pain. When cervical osteochondrosis manifests as pain in the sternum, patients complain of a decrease in muscle strength in the arms.
- In almost every patient with osteochondrosis you can hear a characteristic crunch and cry if you ask the person to turn their head in different directions.
- Roughness of sound. Osteochondrosis of the neck can be manifested by numbness of the tongue, fingertips (a symptom of compression of the nerves and blood vessels near the intervertebral discs.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Paresis of the limbs, a decrease in the strength of the muscles of the limbs.
The cause of the above symptoms is damage to the connective tissue and intervertebral discs with their subsequent deformation. As a result of abnormal processes, the discs proliferate into bone formations, producing osteophytes that suffocate and damage blood vessels and nerve pathways.
Stages of the disease
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops in several stages. The more the patient develops the disease, the more the symptoms become, the more serious the complications of the disease.
Grade 1 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by damage to the pulp of the intervertebral disc nucleus. When the metabolism is disturbed in the body, the nucleus pulposus, which is the structure of biopolymeric compounds, is destroyed. Initially, it loses water, gradually dries out and consequently decreases in size. Its strength is significantly reduced and physical exertion becomes more difficult for the spine. At this stage of the disease a person does not feel pain, does not seek medical help. If you start identifying osteochondrosis at this point, then the patient will not need medication.
Grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by damage to the intervertebral disc anulus fibrosus. As a result of strong and uneven loading of the spine, cracks and tears appear on the surface of the disc. As the anal fibrosis becomes thinner, the nucleus is completely depleted of the resulting tears and cracks, thereby expanding them. As a result, the disc increases in size, beginning to protrude beyond the edges of the spine. This phenomenon is called disc protrusion. Grade 2 osteochondrosis of the cervix is the stage of the disease during which a person first feels pain.
Grade 3 cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by hernia formation. Annulus fibrosus not only thins, but also collapses, so the nucleus pulposus "flows" into the subglottic space and forms a herniated disc. As a result of the development of the process, all the surrounding tissues are affected - the muscles and nerves and blood vessels.
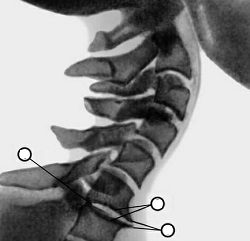
Over time, the skeletal system of the spine changes: the edges of the spine change shape, become ribs, and even sharper. The muscles around the altered bone system contract involuntarily, thus limiting the mobility of the spinal column. All nerve fibers passing through the spinal cord are impaired, disrupting the conduction of nerve impulses from the brain to organs and tissues. It is important that the symptoms of osteochondrosis appear according to the location of the osteochondrosis.
Grade 4 osteochondrosis of the cervix is characterized by degenerative reconstruction of the spine. After the destructive processes in the body, the recovery processes begin. The duration of the fourth stage is about one year. At this time the nature of the growth of the deformed spinal bone changes. The bone begins to grow in width, which is why the malleolus grows. In medicine, such formations are called osteophytes. Thanks to them, the mobility of the damaged spine is reduced and its destruction processes are stopped. Over time, the seated spine completely becomes a static column of bone.And if the pain syndrome is reduced, the crushed nerves and blood vessels remain in place, they are contracted not only by the discs and vertebrae, but also by the formed osteophytes. Such processes must be properly treated to prevent the consequences of disease.
Complications of cervical osteochondrosis The main consequences of developing cervical osteochondrosis are:- vascular disorders (compression of arteries);
- formation of hernias of varying severity;
- spinal cord injury;
- osteophyte formation;
- Restriction of spinal mobility.
What complications can cervical osteochondrosis cause? The most dangerous result is a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain. As a result of the compression of the arteries, less blood enters the brain, the gray matter is poorly supplied with oxygen.
If the patient has developed vertebral artery syndrome - when the main blood flow to the brain is stretched, then the person suffers from dizziness, loses consciousness.
In addition to mental retardation, patients with cervical osteochondrosis have impaired vision and hearing. In addition to numbness of the limbs, it is possible to develop Dupuytren syndrome, which is characterized by hardening of the hands. As a result of the development of the syndrome, the mobility of the fingers is lost.Hypertension and vegetative-vascular dystonia (VVD) are considered common complications. A cosmetic defect that occurs as a result of the development of osteochondrosis is the formation of a peak (a "hill" of cartilage in the back of the head).
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment for cervical osteochondrosis depends on the stage of the disease. Medical treatment includes the appointment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antispasmodics by the doctor. The dose of the drug is adjusted by the decision of the doctor.
Physical therapy is often prescribed to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. With the help of exercise you can not only relieve pain but also reduce inflammation, strengthen spinal muscles and reduce the risk of complications.
Massage has a general strengthening effect. After a course of massage, the patient with osteochondrosis will lose tension and pain and the blood supply will increase.
When medications do not work, doctors must prescribe surgery. During surgery, doctors remove parts of the intervertebral disc that compress the nerve roots.
The best treatment is a combination of several methods. Medical treatment should be combined with massage, exercise and gymnastics.
Some doctors believe that acupuncture and herbal remedies are an effective method of treatment.
Prevention
You can use simple methods to reduce pain and prevent the development of cervical osteochondrosis. To begin with, each person should be constantly in a position that relieves the load on the spinal column. It is necessary to remember about the exercises that relax the muscles and promote metabolic processes in the spine. To get a positive result it is necessary to follow the recommendations given by your doctor.
Key Recommendations:
- Exercise evenly on the spine. To do this, limit vertical loads, avoid sudden movements and exercises that can damage the spinal column. Avoid falling or jumping from great heights.
- Do not carry heavy objects with your arms outstretched in front of you. Before you pick up an object from the floor, you should not turn forward, but sit down.
- Do not move objects with one hand, it is desirable to distribute the load on both limbs. If this is not possible, then load the suitcase with wheels or a backpack.
- If you need to carry heavy loads, then you should wear a wide belt or buy a special corset before work.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- The best prevention of the disease is swimming, regular gymnastics, taking a contrast shower.
- Stressful situations should be avoided.
- You need to remember the rules of a balanced diet.
- Get rid of bad habits.
It is important to understand that the disease is much easier to prevent than to cure it for a long time and persistently. If surgery is not required in the early stages of the disease, then the later stages of osteochondrosis require surgical intervention.



















































